//상속, Inheritance
- 부모가 가지는 재산을 자식에게 물려주는 행동
- 부모(클래스)가 가지는 재산(멤버 변수, 멤버 메서드)을 자식(클래스)에게 물려주는 행동
- 상속하는 이유(목적) : 코드 재사용 > 비용 절감
- 다중 상속 xx
- ★★부모가 물려준 멤버를 자식이 상속 거부할 수 없다. (무조건 모든 것을 다 상속 받아야 함.)
- class A extends B {}
~ A : 자식 클래스, 서브 클래스, 기본 클래스
~ B : 부모 클래스, 슈퍼 클래스, 확장 클래스, 파생 클래스
class B { //부모 클래스
멤버 필드;
멤버 메서드;
}
class A { // 자식 클래스
멤버 필드1;
멤버 메서드1;
}
public class B extends A {
멤버 필드1;
멤버 메서드1;
}
//Phone
package ex01.sample01;
public class Phone {
public String model;
public String color;
public void bell() {
System.out.println("벨이 울린다.");
}
public void sendVoice(String message) {
System.out.println("본인 : " + message);
}
public void receiveVoice(String message) {
System.out.println("상대방 : " + message);
}
public void hangUp() {
System.out.println("전화를 끊습니다.");
}
}
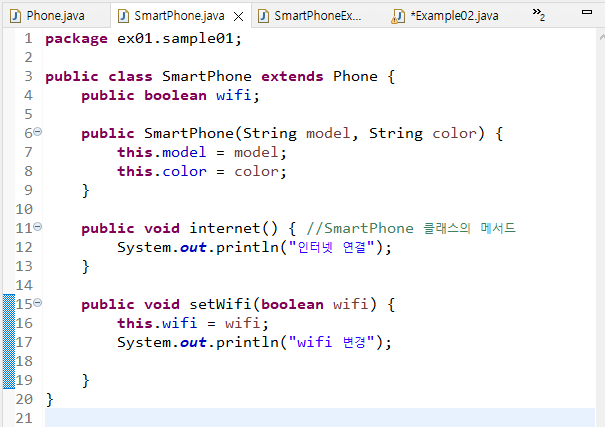
//SmartPhone
package ex01.sample01;
public class SmartPhone extends Phone {
public boolean wifi;
public SmartPhone(String model, String color) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
}
public void internet() { //SmartPhone 클래스의 메서드
System.out.println("인터넷 연결");
}
public void setWifi(boolean wifi) {
this.wifi = wifi;
System.out.println("wifi 변경");
}
}
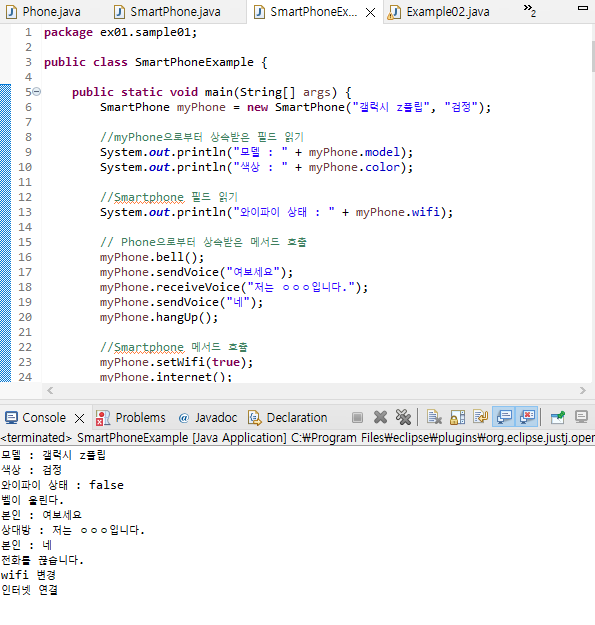
//PhoneExample
package ex01.sample01;
public class SmartPhoneExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SmartPhone myPhone = new SmartPhone("갤럭시 z플립", "검정");
//myPhone으로부터 상속받은 필드 읽기
System.out.println("모델 : " + myPhone.model);
System.out.println("색상 : " + myPhone.color);
//Smartphone 필드 읽기
System.out.println("와이파이 상태 : " + myPhone.wifi);
// Phone으로부터 상속받은 메서드 호출
myPhone.bell();
myPhone.sendVoice("여보세요");
myPhone.receiveVoice("저는 ㅇㅇㅇ입니다.");
myPhone.sendVoice("네");
myPhone.hangUp();
//Smartphone 메서드 호츌
myPhone.setWifi(true);
myPhone.internet();- 부모 클래스의 생성자를 먼저 호출한 후 자식 클래스의 생성자를 호출한다.
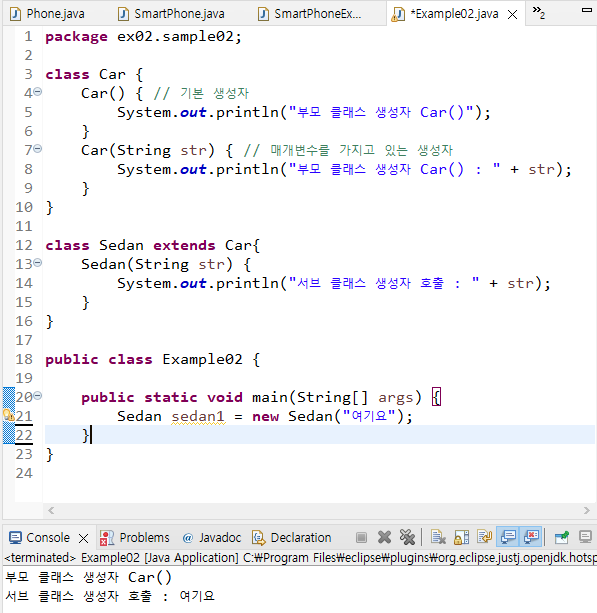
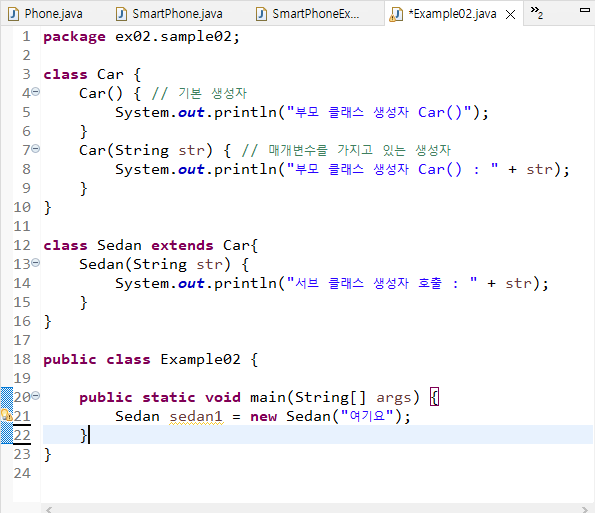
package ex02.sample02;
class Car {
Car() { // 기본 생성자
System.out.println("부모 클래스 생성자 Car()");
}
Car(String str) { // 매개변수를 가지고 있는 생성자
System.out.println("부모 클래스 생성자 Car() : " + str);
}
}
class Sedan extends Car{
Sedan(String str) {
System.out.println("서브 클래스 생성자 호출 : " + str);
}
}
public class Example02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sedan sedan1 = new Sedan("여기요");
}
}// super()
- 부모 클래스를 호출하는 기능 (재정의 x, 그대로 가지고 온 것.)
- 생략 가능하다.(컴파일러가 자동으로 추가함.)
public class A {
String color;
String model;
}
public class B extends A {
public B(String color, String model) { //호출(재정의x)
super(color, model);
....
}// 메서드 오버라이딩
- 기각[무시]하다. 우선하다.
- 자식 클래스가 부모 클래스로부터 상속받은 메서드를 자신에게 맞게 재정의 하는 것
- 오버라이딩 후에는 부모가 선언한 메서드는 호출이 불가능하고, 자식이 오버라이딩한 메서드만 호출 가능
- 메서드 앞에 final을 붙이면 해당 메서드를 오버라이딩 할 수 없다.
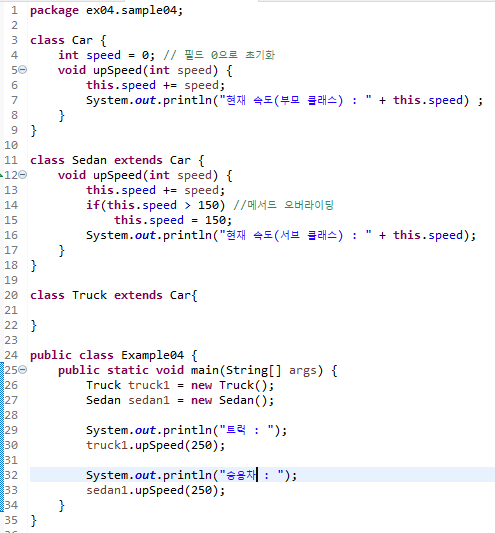
package ex04.sample04;
class Car {
int speed = 0; // 필드 0으로 초기화
void upSpeed(int speed) {
this.speed += speed;
System.out.println("현재 속도(부모 클래스) : " + this.speed) ;
}
}
class Sedan extends Car {
void upSpeed(int speed) {
this.speed += speed;
if(this.speed > 150) //메서드 오버라이딩
this.speed = 150;
System.out.println("현재 속도(서브 클래스) : " + this.speed);
}
}
class Truck extends Car{
}
public class Example04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Truck truck1 = new Truck();
Sedan sedan1 = new Sedan();
System.out.println("트럭 : ");
truck1.upSpeed(250);
System.out.println("승용차 : ");
sedan1.upSpeed(250);
}
}
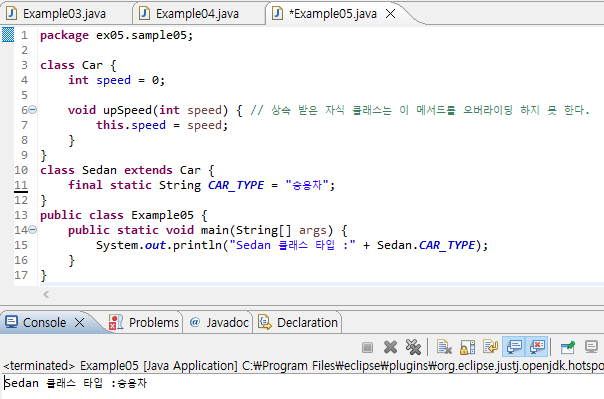
package ex05.sample05;
class Car {
int speed = 0;
void upSpeed(int speed) { // 상속 받은 자식 클래스는 이 메서드를 오버라이딩 하지 못 한다.
this.speed = speed;
}
}
class Sedan extends Car {
final static String CAR_TYPE = "승용차";
}
public class Example05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Sedan 클래스 타입 :" + Sedan.CAR_TYPE);
}
}// super
- this와 같은 역할 > 객체를 가리키는 상대 표현
- 자기 자신(x) > 부모 객체(o)
- 상속 관계에 있는 부모 객체를 가리키는 상대 표현
- 부모(상대 표현)
- 메서드 오버라이딩에 의해 감춰진 부모 메서드 호출
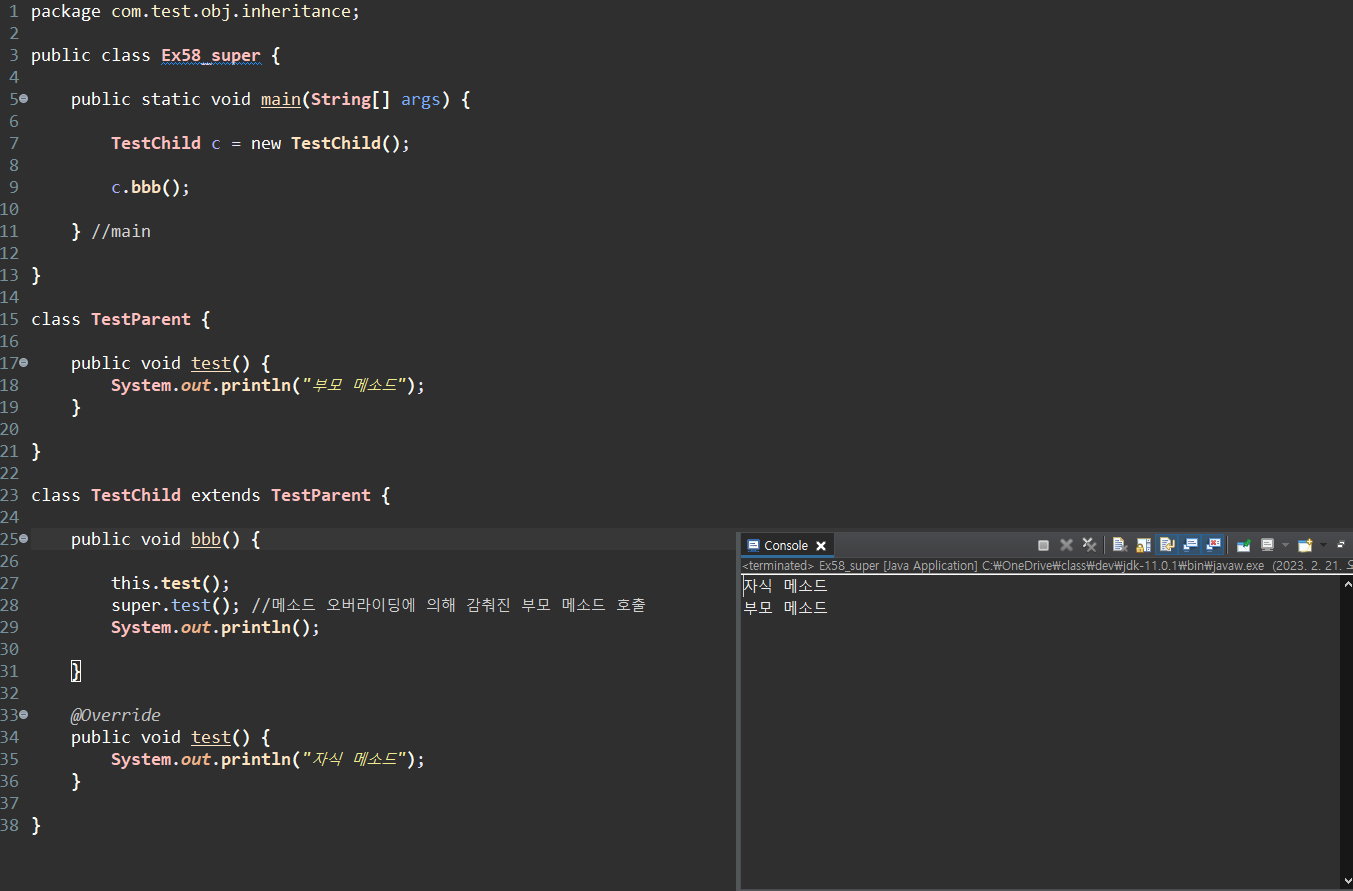
package com.test.obj.inheritance;
public class Ex58_super {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestChild c = new TestChild();
c.bbb();
} //main
}
class TestParent {
public void test() {
System.out.println("부모 메서드");
}
}
class TestChild extends TestParent {
public void bbb() {
this.test();
super.test(); //메서드 오버라이딩에 의해 감춰진 부모 메서드 호출
System.out.println();
}
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("자식 메서드");
}
}//Cating
1. 업캐스팅, Up Casting
- 암시적인 형변환
- 100% 안전
- 자식 클래스 > 부모 클래스
- 부모 클래스 = 자식 클래스;
- 형변환은 되지만, 자식 클래스에는 있고 부모 클래스엔 없는 메서드는 호출할 수 없다.
> 자식 클래스에 있는 메서드를 사용하고 싶다면, 부모 클래스에서 같은 이름의 메서드의 구현부를 비우고 선언한다.
> 오버라이딩 기능 이용
2. 다운캐스팅, Down Casting
- 명시적인 형변환
- 다운캐스팅만 하는 것은 100% 불가능하지만 업캐스팅 후 다시 다운캐스팅 하는 경우는 가능
> 평소에는 형제들과 같이 부모 배열에 넣어서 관리하다가 자식만이 가지는 고유 기능을 사용해야 할 때 다운 캐스팅을 사용해서 원래 타입 참조 변수로 형변환
- 부모 클래스 > 자식 클래스
- 자식 클래스 = 부모 클래스
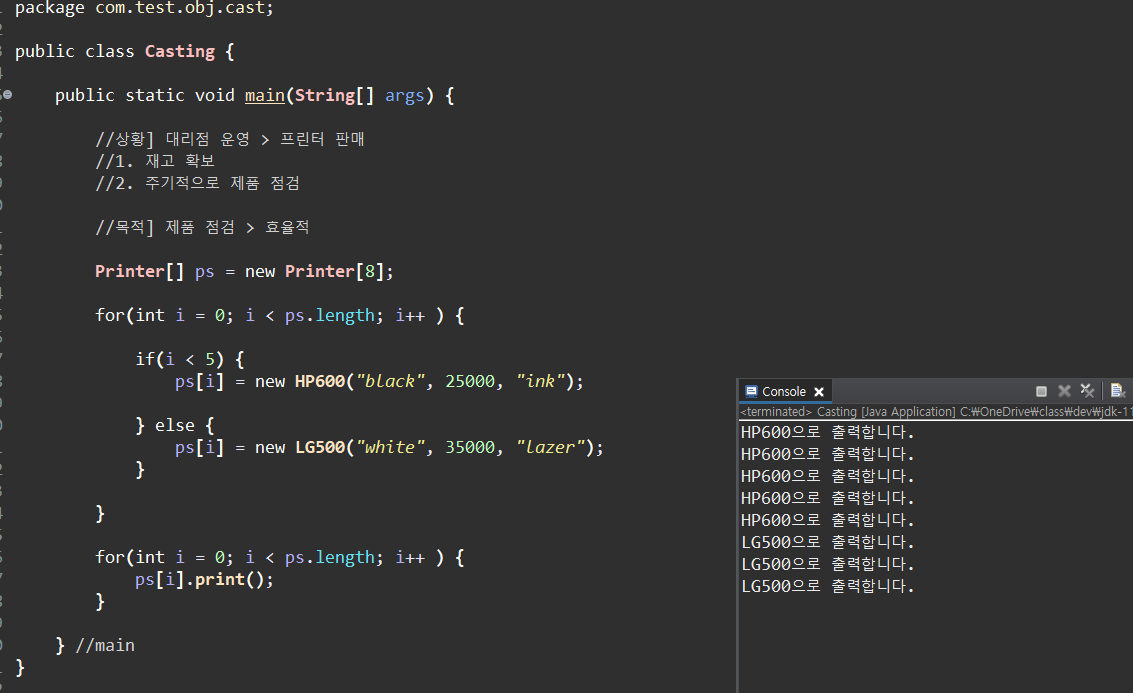
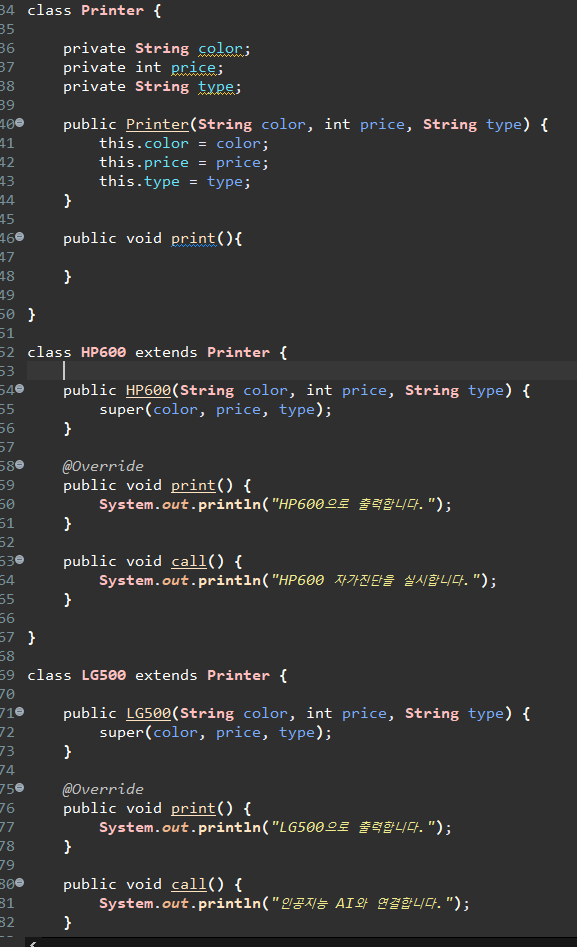
package com.test.obj.cast;
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상황] 대리점 운영 > 프린터 판매
//1. 재고 확보
//2. 주기적으로 제품 점검
//목적] 제품 점검 > 효율적
Printer[] ps = new Printer[8];
for(int i = 0; i < ps.length; i++ ) {
if(i < 5) {
ps[i] = new HP600("black", 25000, "ink");
} else {
ps[i] = new LG500("white", 35000, "lazer");
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < ps.length; i++ ) {
ps[i].print();
}
} //main
}
class Printer {
private String color;
private int price;
private String type;
public Printer(String color, int price, String type) {
this.color = color;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
}
public void print(){
}
}
class HP600 extends Printer {
public HP600(String color, int price, String type) {
super(color, price, type);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("HP600으로 출력합니다.");
}
public void call() {
System.out.println("HP600 자가진단을 실시합니다.");
}
}
class LG500 extends Printer {
public LG500(String color, int price, String type) {
super(color, price, type);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("LG500으로 출력합니다.");
}
public void call() {
System.out.println("인공지능 AI와 연결합니다.");
}
}!Quiz 1!
- Pet이라는 반려동물 클래스를 상속받는 Dog class와 Bird 클래스를 만들어 본다.
- 출력
~ 반려동물이 움직인다.
~ 반려동물이 움직인다.
~ 강아지의 이름은 누렁이, 몸무게는 10kg이다.
~ 새의 종류는 앵무새이고, 날 수 있다.
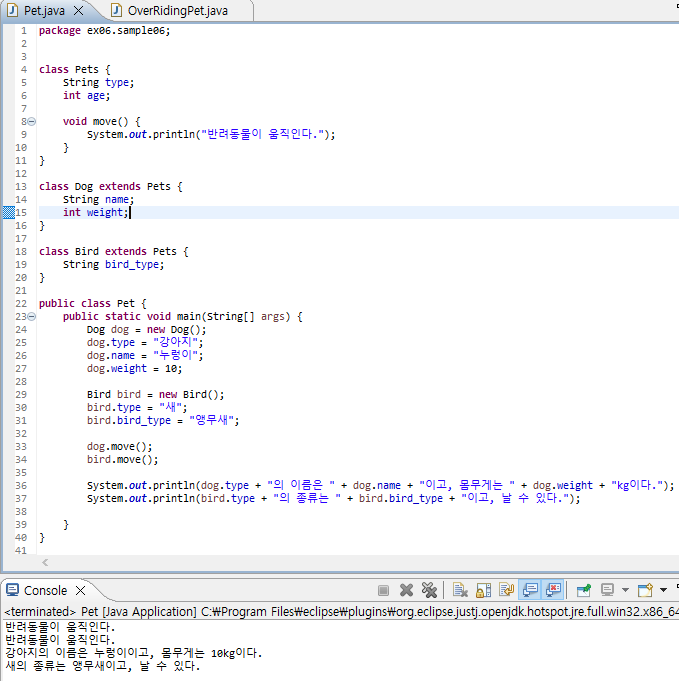
package ex06.sample06;
class Pets {
String type;
int age;
void move() {
System.out.println("반려동물이 움직인다.");
}
}
class Dog extends Pets {
String name;
int weight;
}
class Bird extends Pets {
String bird_type;
}
public class Pet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.type = "강아지";
dog.name = "누렁이";
dog.weight = 10;
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.type = "새";
bird.bird_type = "앵무새";
dog.move();
bird.move();
System.out.println(dog.type + "의 이름은 " + dog.name + "이고, 몸무게는 " + dog.weight + "kg이다.");
System.out.println(bird.type + "의 종류는 " + bird.bird_type + "이고, 날 수 있다.");
}
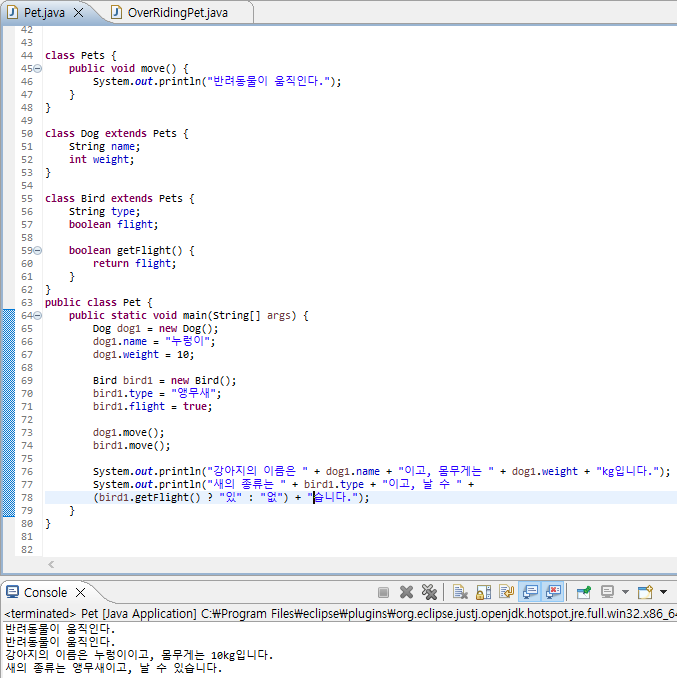
}
package ex06.sample06;
class Pets {
public void move() {
System.out.println("반려동물이 움직인다.");
}
}
class Dog extends Pets {
String name;
int weight;
}
class Bird extends Pets {
String type;
boolean flight;
boolean getFlight() {
return flight;
}
}
public class Pet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
dog1.name = "누렁이";
dog1.weight = 10;
Bird bird1 = new Bird();
bird1.type = "앵무새";
bird1.flight = true;
dog1.move();
bird1.move();
System.out.println("강아지의 이름은 " + dog1.name + "이고, 몸무게는 " + dog1.weight + "kg입니다.");
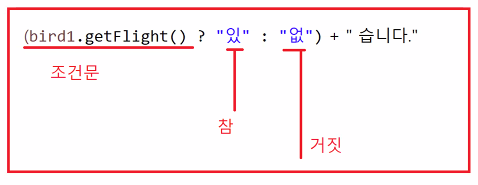
System.out.println("새의 종류는 " + bird1.type + "이고, 날 수 " +
(bird1.getFlight() ? "있" : "없") + "습니다.");
}
}**삼항 연산자
!Quiz 2!
- super class인 Pet 클래스를 상속받는 Dog, Bird 클래스를 작성한다.
~ super class move(): 반려동물이 움직인다.
~ sub class move() : 새가 날아간다.
- move()를 오버라이딩하여 출력하시오.
package ex07.sample07;
class Pets {
String type;
int age;
void move() {
System.out.println("반려동물이 움직인다.");
}
}
class Dog extends Pets {
}
class Bird extends Pets {
String type;
void move() { //앞에 public 붙이기
System.out.println(this.type + "가 날아간다.");
}
}
public class OverRidingPet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.type = "새";
dog.move();
bird.move();
}
}1. 클래스 ==> 일반 클래스
2. 클래스 ==> 추상 클래스
interface를 구현하는 implements
'자바(JAVA)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바(Java)] 추상 클래스, 인터페이스 (0) | 2022.10.13 |
|---|---|
| 이클립스 단축키 (0) | 2022.10.11 |
| [자바(Java)] 선언, 리턴 (0) | 2022.10.06 |
| [자바(Java)] 멤버 필드 vs 지역 변수(로컬 변수) (0) | 2022.10.04 |
| [자바(Java)] 초기화, 메서드 오버로딩 (0) | 2022.09.29 |



