// 초기화의 순서
0. static 키워드
1. 객체 초기화
2. 생성자 초기화
3. 메서드 초기화(메서드 호출 시)
**예외: static(오직 한 번만 초기화)
package ex01.sample01;
class Window {
Window(int marker) {
System.out.println("Window(" + marker + ")");
}
}
class House {
Window w1 = new Window(1);
House() {
System.out.println("House()");
w3 = new Window(33);
}
Window w2 = new Window(2);
void f() {
System.out.println("f()");
}
Window w3 = new Window(3);
}
public class SampleInit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
House h = new House();
h.f();
}
}
Window(1)
Window(2)
Window(3)
House()
Window(22)
f()
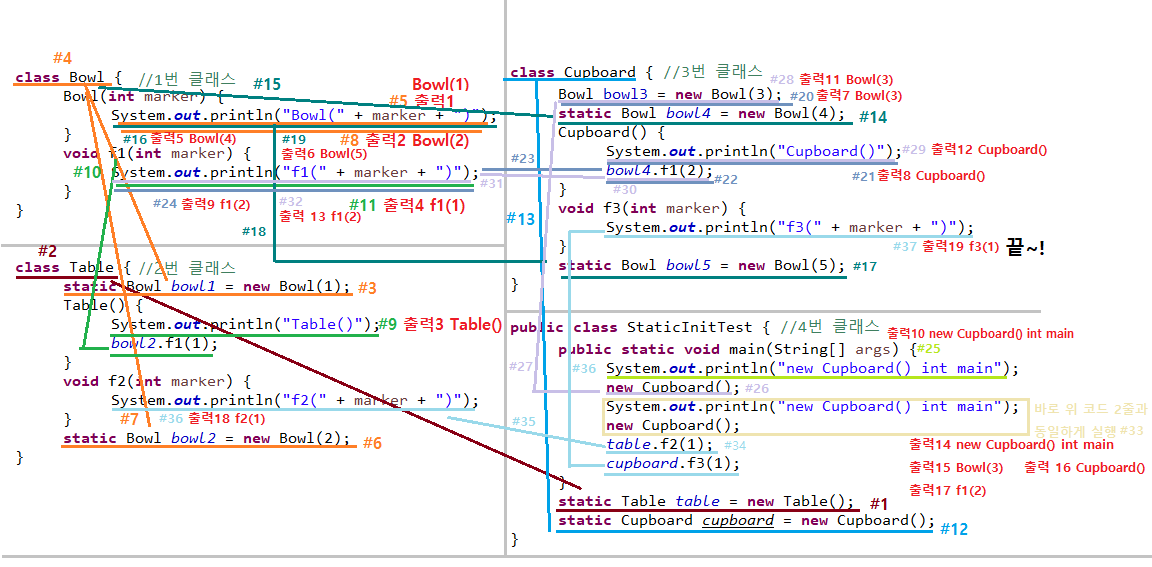
class Bowl {
Bowl(int marker) {
System.out.println("Bowl(" + marker + ")");
}
void f1(int marker) {
System.out.println("f1(" + marker + ")");
}
}
class Table {
static Bowl bowl1 = new Bowl(1);
Table() {
System.out.println("Table()");
bowl2.f1(1);
}
void f2(int marker) {
System.out.println("f2(" + marker + ")");
}
static Bowl bowl2 = new Bowl(2);
}
class Cupboard {
Bowl bowl3 = new Bowl(3);
static Bowl bowl4 = new Bowl(4);
Cupboard() {
System.out.println("Cupboard()");
bowl4.f1(2);
}
void f3(int marker) {
System.out.println("f3(" + marker + ")");
}
static Bowl bowl5 = new Bowl(5);
}
public class StaticInitTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("new Cupboard() int main");
new Cupboard();
System.out.println("new Cupboard() int main");
new Cupboard();
table.f2(1);
cupboard.f3(1);
}
static Table table = new Table();
static Cupboard cupboard = new Cupboard();
}
Bowl(1)
Bowl(2)
Table()
f1(1)
Bowl(4)
Bowl(5)
Bowl(3)
Cupboard()
f1(2)
new Cupboard() int main
Bowl(3)
Cupboard()
f1(2)
new Cupboard() int main
Bowl(3)
Cupboard()
f1(2)
f2(1)
f3(1)
** 반환 값이 없을 때는 void형으로 메서드 선언, 있을 때는 값의 데이터 형으로 선언
//★★스태틱(static) : 정적 초기화
- 한 번 호출하면 다시 초기화하지 않아도 됨. (static 필드는 메모리에 오직 하나만 존재)
<===> this-동적 초기화 (같은 블럭에서 사용할 수 없다.)
- ★★지역 변수에는 static 키워드를 사용할 수 없다.(클래스의 멤버 필드에만 사용 가능!!)
- 사용자 정의 메서드에는 항상 static이 붙는다.

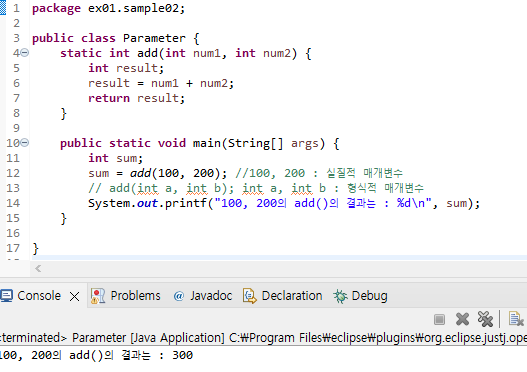
package ex01.sample02;
public class Parameter {
static int add(int num1, int num2) {
int result;
result = num1 + num2;
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum;
sum = add(100, 200); //100, 200 : 실질적 매개변수
// add(int a, int b); int a, int b : 형식적 매개변수
System.out.printf("100, 200의 add()의 결과는 : %d\n", sum);
}
}자바에서는 'static 구문(블록)'을 이용하여 변수 초기화가 가능하다.
static int i;
static {
i = 47;
}위 코드도 일반적인 static 초기화와 같이 한 번만 실행한다.
// 변수 초기화
- 일반적으로 지역 변수는 사용자가 선언과 동시에 초기화, 전역 변수는 선언을 해주면 자동으로 초기화됨.
- 자바에서는 필드(클래스가 가지고 있는 변수)는 자동 초기화
| 정수 타입 | 0 |
| 문자 타입 | \0(빈 공백) |
| 실수 타입 | 0.0 |
| 논리 타입 | false |
| 참조 타입 | null |
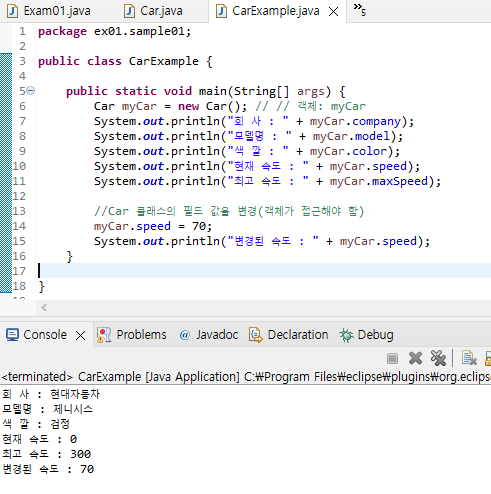
package ex01.sample01;
public class CarExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car(); // // 객체: myCar
System.out.println("회 사 : " + myCar.company);
System.out.println("모델명 : " + myCar.model);
System.out.println("색 깔 : " + myCar.color);
System.out.println("현재 속도 : " + myCar.speed);
System.out.println("최고 속도 : " + myCar.maxSpeed);
//Car 클래스의 필드 값을 변경(객체가 접근해야 함)
myCar.speed = 70;
System.out.println("변경된 속도 : " + myCar.speed);
}
}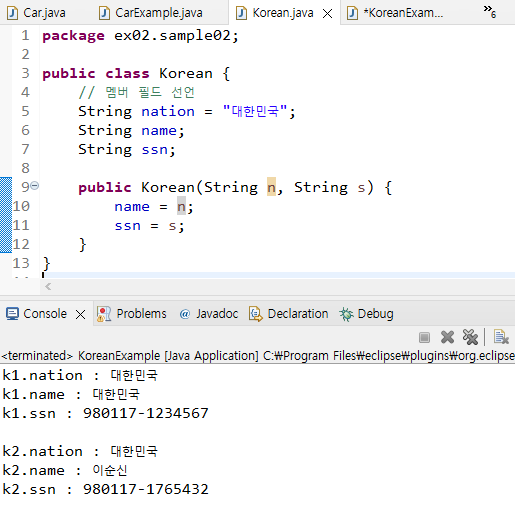
package ex02.sample02;
public class Korean {
// 멤버 필드 선언
String nation = "대한민국";
String name;
String ssn;
public Korean(String n, String s) {
name = n;
ssn = s;
}
}
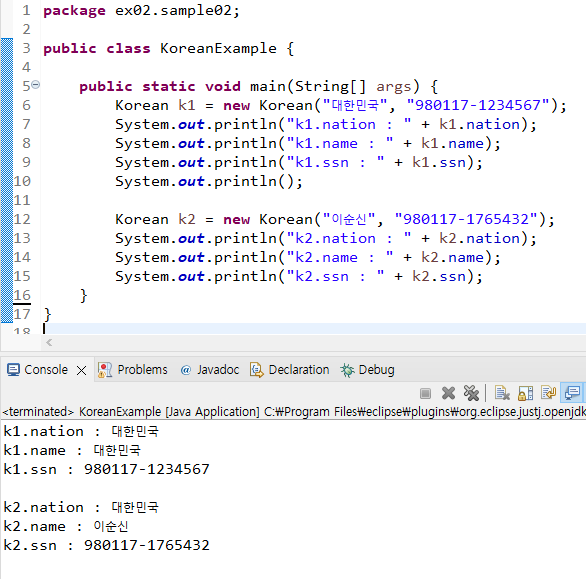
package ex02.sample02;
public class KoreanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Korean k1 = new Korean("대한민국", "980117-1234567");
System.out.println("k1.nation : " + k1.nation);
System.out.println("k1.name : " + k1.name);
System.out.println("k1.ssn : " + k1.ssn);
System.out.println();
Korean k2 = new Korean("이순신", "980117-1765432");
System.out.println("k2.nation : " + k2.nation);
System.out.println("k2.name : " + k2.name);
System.out.println("k2.ssn : " + k2.ssn);
}
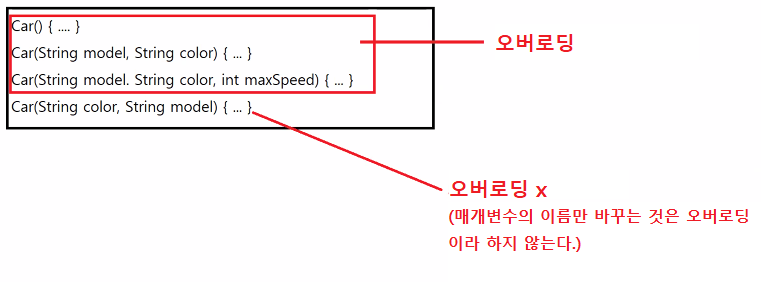
}// 오버로딩
- 자바의 한 클래스 내에 이미 사용하려는 이름과 같은 이름을 가진 메서드가 또 있는 것
- 동일한 이름 메서드 가 인자 리스트를 다양하게 가지면서 여러 개 선언하는 기술
- 성능 향상x, 개발자에게 도움o > 메서드 이름을 외우기 편함.
- 메서드 오버로딩 구현 조건 > 가능
1. 매개변수의 개수
2. 매개변수의 자료형
- 메서드 오버로딩 구현 조건 > 불가능
1. 매개변수의 이름
2. 반환 값의 자료형
~ public static void test() {}
~ public static void test() {} //x
~ public static void test(int n){} //o
~ public static void test(int m){} //x
~ public static void test(Stirng s){} //o
~ public static void test(int n, int m){} //o
- this : 객체를 지시(지정)하는 것
- 클래스 멤버 필드와 생성자 매개변수의 이름이 같은 경우 this를 이용하여 멤버필드를 지정해줄 수 있음.
~ 생성자뿐만 아니라 메서드도 오버로딩 有
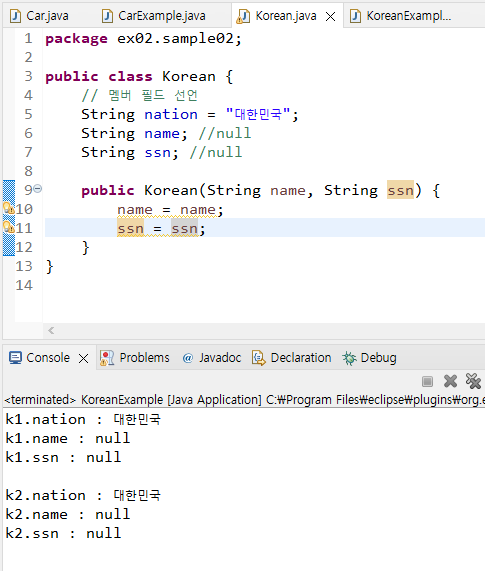
package ex02.sample02;
public class Korean {
// 멤버 필드 선언
String nation = "대한민국";
String name; //null
String ssn; //null
public Korean(String name, String ssn) {
name = name;
ssn = ssn;
}
}
package ex02.sample02;
public class KoreanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Korean k1 = new Korean("대한민국", "980117-1234567");
System.out.println("k1.nation : " + k1.nation);
System.out.println("k1.name : " + k1.name);
System.out.println("k1.ssn : " + k1.ssn);
System.out.println();
Korean k2 = new Korean("이순신", "980117-1765432");
System.out.println("k2.nation : " + k2.nation);
System.out.println("k2.name : " + k2.name);
System.out.println("k2.ssn : " + k2.ssn);
}
}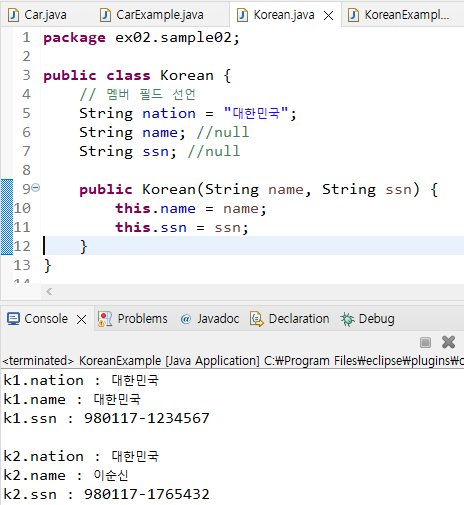
package ex02.sample02;
public class Korean {
// 멤버 필드 선언
String nation = "대한민국";
String name; //null
String ssn; //null
public Korean(String name, String ssn) {
this.name = name;
this.ssn = ssn;
}
}
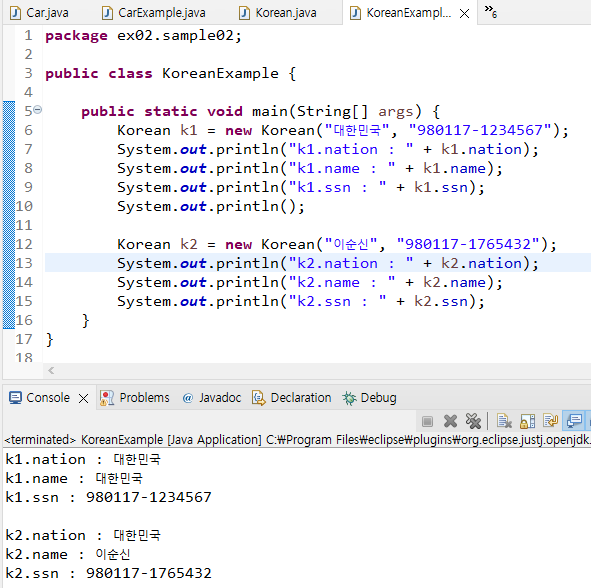
package ex02.sample02;
public class KoreanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Korean k1 = new Korean("대한민국", "980117-1234567");
System.out.println("k1.nation : " + k1.nation);
System.out.println("k1.name : " + k1.name);
System.out.println("k1.ssn : " + k1.ssn);
System.out.println();
Korean k2 = new Korean("이순신", "980117-1765432");
System.out.println("k2.nation : " + k2.nation);
System.out.println("k2.name : " + k2.name);
System.out.println("k2.ssn : " + k2.ssn);
}
}
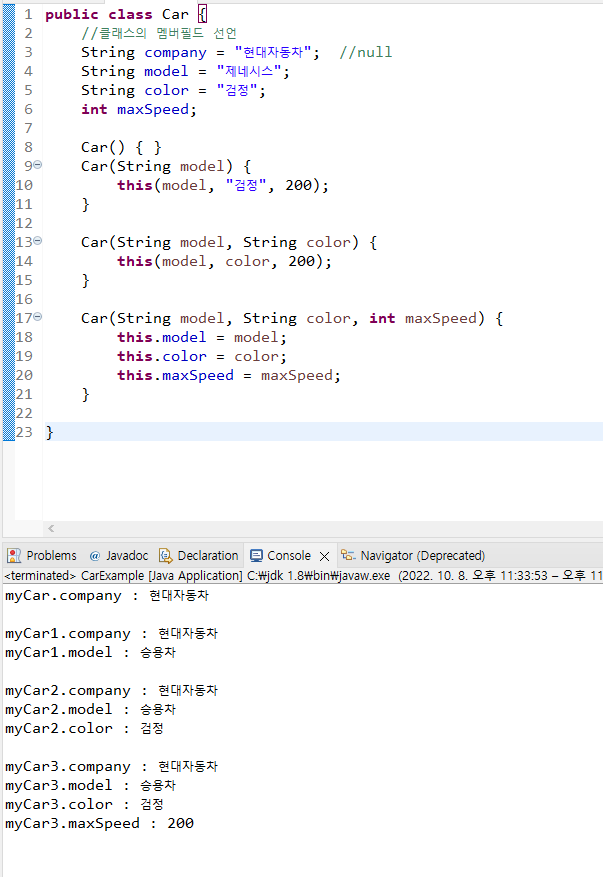
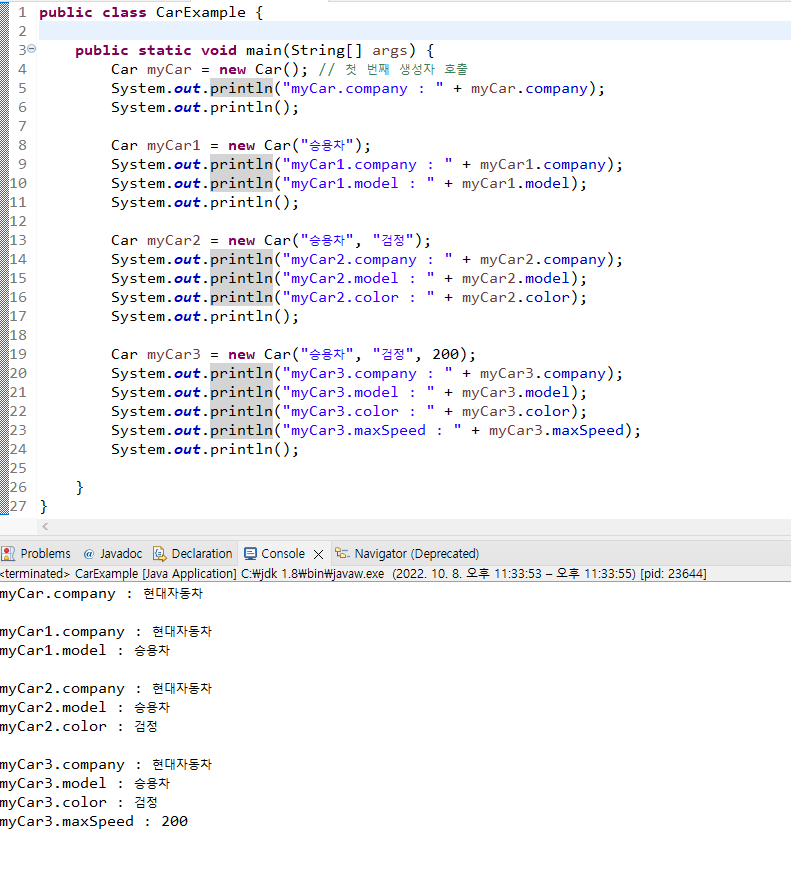
public class Car {
//클래스의 멤버필드 선언
String company = "현대자동차"; //null
String model = "제네시스";
String color = "검정";
int maxSpeed;
Car() { }
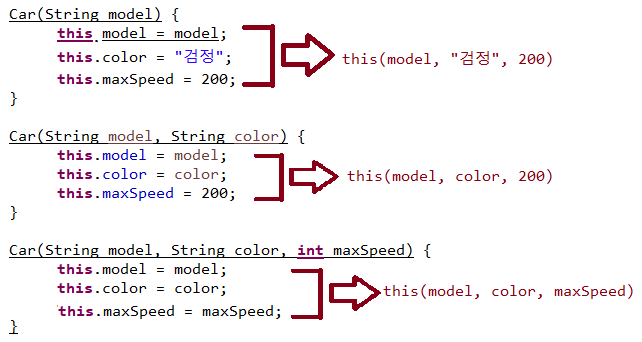
Car(String model) {
this(model, "검정", 200);
}
Car(String model, String color) {
this(model, color, 200);
}
Car(String model, String color, int maxSpeed) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
}
public class CarExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car(); // 첫 번째 생성자 호출
System.out.println("myCar.company : " + myCar.company);
System.out.println();
Car myCar1 = new Car("승용차");
System.out.println("myCar1.company : " + myCar1.company);
System.out.println("myCar1.model : " + myCar1.model);
System.out.println();
Car myCar2 = new Car("승용차", "검정");
System.out.println("myCar2.company : " + myCar2.company);
System.out.println("myCar2.model : " + myCar2.model);
System.out.println("myCar2.color : " + myCar2.color);
System.out.println();
Car myCar3 = new Car("승용차", "검정", 200);
System.out.println("myCar3.company : " + myCar3.company);
System.out.println("myCar3.model : " + myCar3.model);
System.out.println("myCar3.color : " + myCar3.color);
System.out.println("myCar3.maxSpeed : " + myCar3.maxSpeed);
System.out.println();
}
}
'자바(JAVA)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자바(Java)] 선언, 리턴 (0) | 2022.10.06 |
|---|---|
| [자바(Java)] 멤버 필드 vs 지역 변수(로컬 변수) (0) | 2022.10.04 |
| [자바(Java)] 사용자 입력(Console input) (0) | 2022.09.27 |
| [자바(Java)] String (1) | 2022.09.23 |
| [자바(Java)] 배열(Arrays) (0) | 2022.09.22 |



